|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
TCP/IP Remote Network Monitoring (RMON)
(Page 2 of 3)
RMON MIB Hierarchy and Object Groups
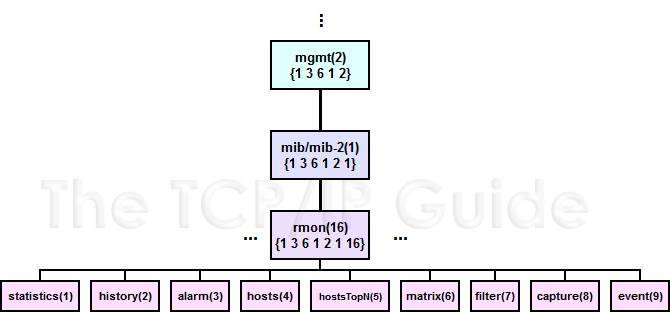
Since RMON is a MIB module, it consists almost entirely of descriptions for MIB objects, with each having the standard characteristics belonging to all such objects. All the objects within RMON are arranged into the SNMP object name hierarchy within the rmon group, which is group number 16 within the SNMP mib (mib-2) object tree, 1.3.6.1.2.1. So, all RMON objects have identifiers starting with 1.3.6.1.2.1.16. This single RMON group is broken down into several lower-level groups that provide more structure for the RMON objects defined by the specification. Figure 286 shows this structure.
|
Table 222 describes each of the RMON groups, showing for each its name, its group code (which is used as the prefix for object descriptors in the group), and its RMON group number and SNMP object hierarchy identifier:
RMON Group Name |
RMON Group Code |
RMON Group Number |
Full Group Identifier |
Description |
statistics |
etherStats |
1 |
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1 |
Objects that keep track of network statistics measured by the device. Example statistics include network traffic load, average packet size, number of broadcasts observed, counts of errors that have occurred, the number of packets in various size ranges and so forth. |
history |
history, etherHistory |
2 |
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.2 |
The history group contains a single table object that controls how often statistical data is sampled by the probe. The additional etherHistory group is optional and contains extra Ethernet-specific information; it is contained logically within the history group. |
alarm |
alarm |
3 |
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3 |
This group defines the parameters under which an alarm may be generated to inform an administrator of an occurrence of import. The alarm group contains a table that describes the thresholds that will cause an event to be triggered (see the event group below). |
hosts |
host |
4 |
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.4 |
Contains objects that keep track of information for each host on a network. |
hostsTopN |
hostTopN |
5 |
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.5 |
This group contains objects that facilitate reporting of hosts sorted in a particular way. The administrator determines how these ordered statistics are tracked. For example, an administrator could generate a report listing hosts sorted by the number of packets transmitted, showing the most active devices. |
matrix |
matrix |
6 |
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.6 |
This group keeps track of statistics for data exchanges between particular pairs of hosts. So, the amount of data sent between any two devices on the network could be tracked here. Since a large network could have thousands of such device pairs, to conserve resources on the probe, often only the most recent “conversations” between device pairs are kept in the management information base. |
filter |
filter |
7 |
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.7 |
This RMON group allows an administrator to set up filters that control what sorts of network packets the probe will capture. |
capture |
buffer, capture |
8 |
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.8 |
This group is used to allow a probe to capture packets based on particular parameters set up in the filter group. |
event |
event |
9 |
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.9 |
When a particular alarm is triggered based on the parameters in the objects in the alarm group, an event is generated. This group controls how these events are processed, including creating and sending an SNMP trap message to a network monitoring station. |
The original RMON standard was heavily oriented around Ethernet LANs, and you can see some of that in the table above. Probes can also gather and report information related to other networking technologies, by using other RMON groups created for that purpose. The best example of this was the definition of a set of groups specifically for Token Ring, which was defined in RFC 1513 in 1993.
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.