 |
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
Mobile IP Addressing: Home and "Care-Of" Addresses
(Page 1 of 2)
Just as most of us have only a single address used for our mail, most IP devices have only a single address. Our traveling consultant, however, needs to have two addresses; a normal one and one that is used while he is away. Continuing our earlier analogy, the Mobile-IP-equipped notebook our consultant carries needs to have two addresses as well:
- Home Address: The “normal”,
permanent IP address assigned to the mobile node. This is the address
used by the device on its home network, and the one to which datagrams
intended for the mobile node are always sent.
- Care-Of Address: A secondary, temporary address used by a mobile node while it is 'traveling” away from its home network. It is a normal 32-bit IP address in most respects, but is used only by Mobile IP for forwarding IP datagrams and for administrative functions. Higher layers never use it, nor do regular IP devices when creating datagrams.
The care-of address is a slightly tricky concept. There are two different types, which correspond to two distinctly different methods of forwarding datagrams from the home agent router.
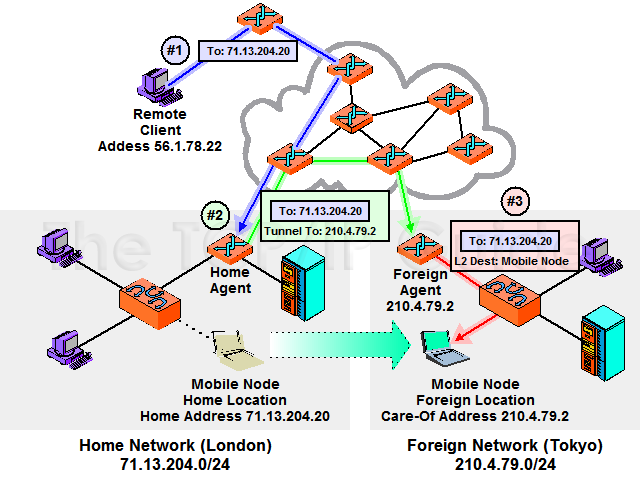
This is a care-of address provided by a foreign agent in its Agent Advertisement message. It is, in fact, the IP address of the foreign agent itself. When this type of care-of address is used, all datagrams captured by the home agent are not relayed directly to the mobile node, but indirectly to the foreign agent, which is responsible for final delivery. Since in this arrangement the mobile node has no distinct IP address valid on the foreign network, this is typically done using a layer two technology. This arrangement is illustrated in Figure 129.
In our consultant analogy, this type of care-of address is like forwarding from the London post office to the Tokyo post office. The London personnel would take a letter for John Smith sent to his London address, and repackage it for delivery to “John Smith, care of the Tokyo post office”. The Tokyo post office (or John Smith himself) would need to worry about the last leg of the delivery.
This is a care-of address assigned directly to the mobile node using some means external to Mobile IP. For example, it may be assigned on the foreign network manually, or automatically using DHCP. In this situation, the care-of address is used to forward traffic from the home agent directly to the mobile node. This was the type of address shown in Figure 128.
In our consultant analogy, this is like John Smith obtaining a temporary address for his use while in Tokyo. The London post office would forward directly to his Tokyo address. They would not specifically send it to the Tokyo post office (though of course that PO would handle the mail at some point).
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







 Key Concept: In Mobile IP, each mobile device uses a temporary, care-of address while on a foreign network. A co-located care-off address is one that is assigned directly to the mobile node, and enables direct delivery of datagrams to the node. The alternative is to use a foreign agent care-of address. In this situation the mobile node actually uses the IP address of the foreign agent; datagrams are sent to the foreign agent, which delivers them to the mobile node.
Key Concept: In Mobile IP, each mobile device uses a temporary, care-of address while on a foreign network. A co-located care-off address is one that is assigned directly to the mobile node, and enables direct delivery of datagrams to the node. The alternative is to use a foreign agent care-of address. In this situation the mobile node actually uses the IP address of the foreign agent; datagrams are sent to the foreign agent, which delivers them to the mobile node.