|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
IP Basic Address Structure and Main Components: Network ID and Host ID
(Page 1 of 3)
As I mentioned in the IP addressing overview, one of the ways that IP addresses are used is to facilitate the routing of datagrams in an IP internet. This is made possible because of the way that IP addresses are structured, and how that structure is interpreted by network routers.
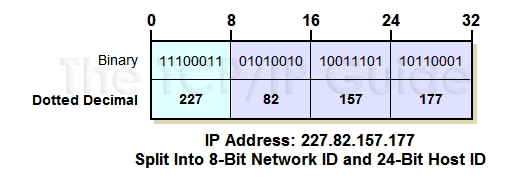
As we just saw, each version 4 IP address is 32 bits long. When we refer to the IP address we use a dotted-decimal notation, while the computer converts this into binary. However, even though these sets of 32 bits are considered a single “entity”, they have an internal structure containing two components:
- Network Identifier (Network ID): A certain
number of bits, starting from the left-most bit, is used to identify
the network where the host or other network interface is located. This
is also sometimes called the network prefix or even just the
prefix.
- Host Identifier (Host ID): The remainder of the bits are used to identify the host on the network.
|
As you can see in Figure 57, this really is a fairly simple concept; it's the same idea as the structure used for phone numbers in North America. The telephone number (401) 555-7777 is a ten-digit number usually referred to as a single “phone number”. However, it has a structure. In particular, it has an area code (“401”) and a local number (“555-7777”).
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







 Note: By convention, IP devices are often called hosts for simplicity, as I do throughout this Guide. Even though each host usually has a single IP address, remember that IP addresses are strictly associated with network-layer network interfaces, not physical devices, and a device may therefore have more than one IP address.
Note: By convention, IP devices are often called hosts for simplicity, as I do throughout this Guide. Even though each host usually has a single IP address, remember that IP addresses are strictly associated with network-layer network interfaces, not physical devices, and a device may therefore have more than one IP address.