 |
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
BGP Route Information Exchange: Update Messages
(Page 2 of 2)
BGP Update Message Format
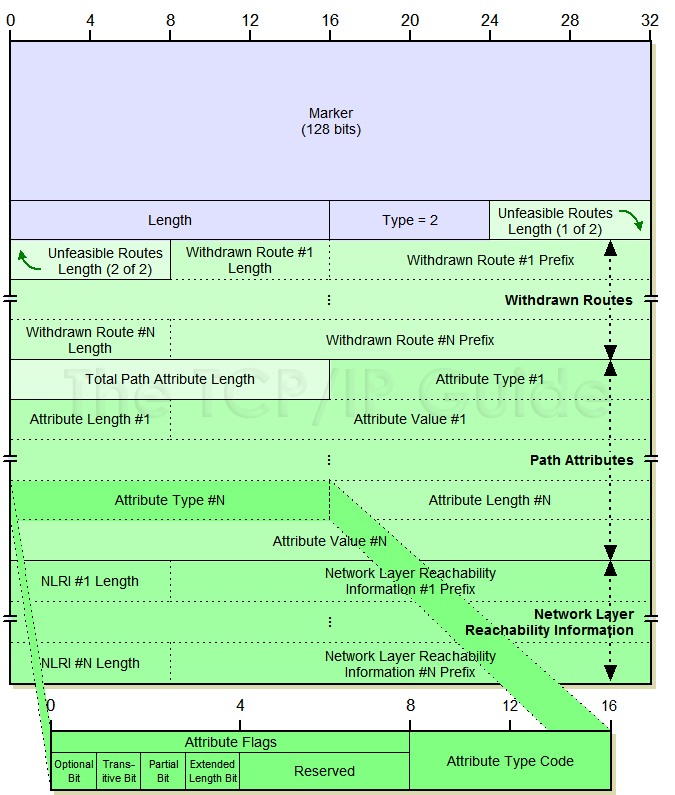
Because of the amount of information it contains, and the complexity of that information, BGP Update messages use one of the most complicated structures in all of TCP/IP. The basic structure of the message is described in Table 138, and illustrated in Figure 194. As you can see in that table, several of the fields have their own substructure. The Attribute Type subfield of the Path Attributes field has itself a complex substructure, which I have shown separately in Table 139 to avoid overloading Table 138.
When you examine this format, you may find it confusing that there can be more than one prefix in the NLRI field, given that I just said that an Update message advertises only one route. There is in fact no inconsistency here. A single route may be associated with more than one network; or, to put it another way, multiple networks may have the same path and path attributes. In that case, specifying multiple network prefixes in the same Update is more efficient than generating a new one for each network.
Field Name |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
Marker |
16 |
Marker: This large field at the start of each BGP message is used for synchronization and authentication. See the discussion of the BGP general message format for details. |
Length |
2 |
Length: The total length of the message in bytes, including the fields of the header. Update messages are variable in length. |
Type |
1 |
Type: BGP message type, value is 2 for Update messages. |
Unfeasible Routes Length |
2 |
Unfeasible Routes Length: The length of the Withdrawn Routes field, in bytes. If 0, no routes are being withdrawn and the Withdrawn Routes field is omitted. |
Withdrawn Routes |
Variable |
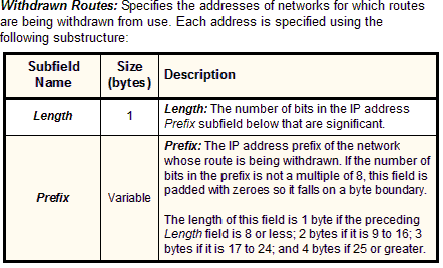
|
Total Path Attribute Length |
2 |
Total Path Attribute Length: The length of the Path Attributes field, in bytes. If 0, indicates no route is being advertised in this message, so Path Attributes and Network Layer Reachability Information are omitted. |
Path Attributes |
Variable |
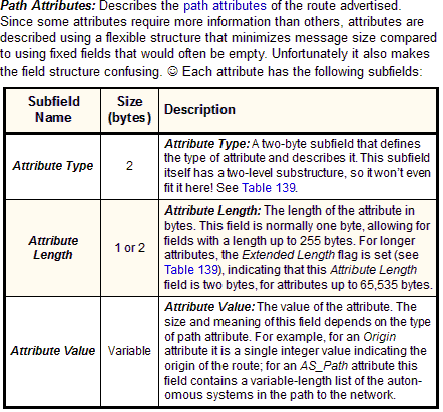
|
Network Layer Reachability Information |
Variable |
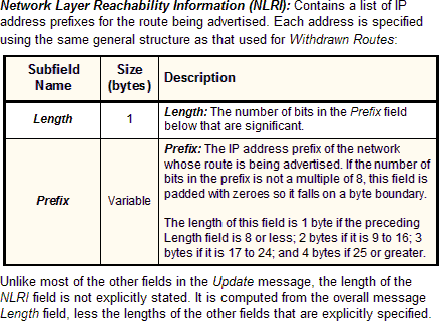
|
|
Sub-subfield Name |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
Attribute Flags |
1 |
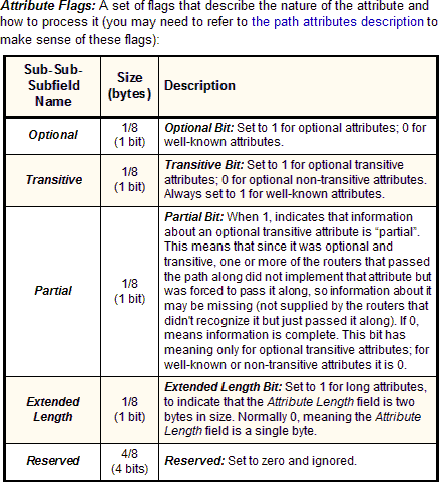
|
Attribute Type Code |
1 |
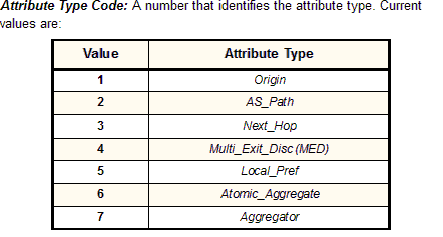
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







 Key Concept: The most important message type in BGP is the Update message, which is used to send detailed information about routes between BGP devices. It uses a complex structure that allows a BGP speaker to efficiently specify new routes, update existing ones, and withdraw routes that are no longer valid. Each message may include the full description of one existing route, and may also withdraw from use a list of multiple routes.
Key Concept: The most important message type in BGP is the Update message, which is used to send detailed information about routes between BGP devices. It uses a complex structure that allows a BGP speaker to efficiently specify new routes, update existing ones, and withdraw routes that are no longer valid. Each message may include the full description of one existing route, and may also withdraw from use a list of multiple routes.